- Brefeldin A
-
Strukturformel 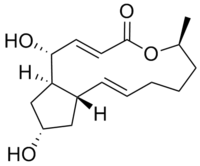
Allgemeines Name Brefeldin A Andere Namen - γ,4-Dihydroxy-2-(6-hydroxy-1-heptenyl)-4-cyclopentanecrotonic-acid-λ-lacton
Summenformel C16H14O4 CAS-Nummer 20350-15-6 PubChem 5287620 Kurzbeschreibung weißes bis gelbweißes kristallines Pulver [1]
Eigenschaften Molare Masse 280,36 g·mol–1 Aggregatzustand fest
Sicherheitshinweise GHS-Gefahrstoffkennzeichnung [1] 
Gefahr
H- und P-Sätze H: 301 EUH: keine EUH-Sätze P: 301+310 [1] EU-Gefahrstoffkennzeichnung [1] 
Gesundheits-
schädlich(Xn) R- und S-Sätze R: 22 S: keine S-Sätze LD50 Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Brefeldin A (Abkürzung: BFA) ist ein Lacton-Antibiotikum, das von Pilzen wie Eupenicillium brefeldianum synthetisiert wird und ursprünglich als ein antivirales Therapeutikum isoliert wurde.[2] Heutzutage wird es hauptsächlich in der medizinischen und biologischen Forschung zur Untersuchung des Proteintransportes eingesetzt.[3]
BFA interferiert im retrograden Transport vom Golgi-Apparat zum Endoplasmatischen Retikulum, wodurch es zu einer Akkumulation von Proteinen (zum Beispiel von Interferon γ) im Endoplasmatischen Retikulum kommt. Brefeldin A scheint dabei an einem bestimmten GTP-Austauschfaktor anzugreifen, der für die Aktivierung der GTPase Arf1p verantwortlich ist.[4]
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Physikalische Eigenschaften
- Klare, farblose Lösung in 10 mg/ml Dichlormethan.
- Klare, farblose Lösung in 10 mg/ml Methanol.[5]
Die Wirkung von Brefeldin A
Brefeldin A wirkt in kürzester Zeit als Zellgift: Der Golgi-Apparat zerfällt und wandelt sich zum Endoplasmatischen Retikulum (ER). [6] Wegen dieser Charakteristik ist Brefeldin ein wirksamer Hemmstoff der Sekretion einer Zelle: Proteine, die sezerniert werden sollen, werden im ER translatiert, reifen im Golgi und in Post-Golgi-Kompartimenten und werden schließlich durch Vesikelfusion mit der Zellmembran freigesetzt.
Brefeldin A hemmt Proteine, die ADP-Ribosylierungsfaktoren aktivieren, die sogenannte Arfs. Im ER werden durch kleine, GTP-beladene G-Proteine der Arf-Familie Protein-Komplexe organisiert, sogenannte Coats. Die Coats helfen, notwendige Transportmoleküle auszuwählen und wirken als Gerüst, an dem Vesikel abgeschnürt werden.[7] Auf dem Weg vom ER zum Golgi hin werden solche Vesikel erst vom ER abgeschnürt und dann in den Golgi eingelagert (Zisternenreifung oder anterograder Transport); umgekehrt werden in gleicher Weise auch Proteine in Vesikeln zur Wiederverwendung vom Golgi zurück zum ER geschleust (retrograder Transport).[8] Die Bildung solcher Vesikel hängt von der COP-I-Zusammenlagerung durch Arf1-GTP ab. Brefeldin-A-Hemmung von Arf1 löst die COP-I-Vesikel auf, läßt den Golgi kollabieren und lagert die betroffenen Proteine wieder in das ER ein. [6]
Durch GTP-spaltende GTPase wird das aktive Arf1-GTP zum inaktiven Arf1-GDP umgewandelt. Arf1-GPD wiederum tauscht, vermittelt durch Sec7-GDP-GTP-Austauschfaktoren, GDP wieder gegen GTP aus. Brefeldin A blockiert den GDP-GTP-Austausch, indem es den Arf1-GPD:Sec7-Komplex stabilisiert und damit inaktiviert.[9] Dies war das erste Beispiel dafür, dass ein Toxin ein Protein in einer Falle fängt und so seine Funktion eliminiert. [10]
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b c d e Datenblatt Brefeldin A bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 14. März 2011.
- ↑ Tamura G, Ando K, Suzuki S, Takatsuki A, Arima K: Antiviral activity of brefeldin A and verrucarin A. In: J. Antibiot.. 21, Nr. 2, Februar 1968, S. 160–161. PMID 4299889.
- ↑ Klausner RD, Donaldson JG, Lippincott-Schwartz J: Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. In: J. Cell Biol.. 116, Nr. 5, März 1992, S. 1071–80. doi:10.1083/jcb.116.5.1071. PMID 1740466. Volltext bei PMC: 2289364.
- ↑ Rajamahanty S, Alonzo C, Aynehchi S, Choudhury M, Konno S: Growth inhibition of androgen-responsive prostate cancer cells with brefeldin A targeting cell cycle and androgen receptor. In: Journal of Biomedical Science. 17, Nr. 1, 2010, S. 5. doi:10.1186/1423-0127-17-5. PMID 20102617. Volltext bei PMC: 2843609. Abgerufen am 29. März 2010..
- ↑ Physikalische Eigenschaften: Brefeldin A − Produktinformation der Firma Fermentek
- ↑ a b J Cell Biol. 1997 Dec 1;139(5):1137-55. Golgi tubule traffic and the effects of brefeldin A visualized in living cells. Sciaky N, Presley J, Smith C, Zaal KJ, Cole N, Moreira JE, Terasaki M, Siggia E, Lippincott-Schwartz J.
- ↑ Schekman, R., and Orci, L. (1996). Science 271, 1526-1533.
- ↑ Glick, B.S., and Malhotra, V. (1998). Cell 95, 883–889
- ↑ Peyroche, A., Antonny, B., Robineau, S., Acker, J., Cherfils, J., Jackson, C.L. (1999). Mol. Cell 3, 275–285.
- ↑ Cell, Vol. 97, 153–155, April 16, 1999, P. Chardin und F. McCormick, Brefeldin A: the advantage of being uncompetitive
Weblinks
- NCI Frederick: Structure and Data for Brefeldin A (NSC 56310) (Strukturformel)
Wikimedia Foundation.
