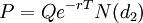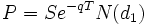- Digital option
-
Digitale Optionen (oder Binäre Optionen, Bet Optionen) sind Finanzderivate die von Optionen abgeleitet sind und zählen zu den exotischen Optionen.
Cash-or-Nothing-Option
Cash-or-Nothing-Optionen sind Optionen mit einem festgelegten Auszahlungsbetrag (auch Payoff oder Cap). Der Käufer einer Kaufoption (Call) erhält im Verfallszeitpunkt nichts (Option verfällt), wenn der Kurs des Basiswerts unterhalb des Basispreises liegt. Ist der Basiskurs über oder gleich dem Basispreis, erhält der Käufer der Option den Vereinbarten Payoff. Eine Verkaufsoption (Put) verhält sich umgekehrt. Der Käufer erhält den Payoff dann nur wenn der Basiskurs im Verfallszeitpunkt unter oder gleich dem Basispreis liegt, andernfalls verfällt die Option.
Beispiel: Eine Cash-or-Nothing-Kaufoption auf den Basispreis X = 100 einer Aktie A mit einer Laufzeit von T = 1 Jahr und einem Payoff von Q = 10 ist folgendes Wert:
- Hat die Aktie A zum Laufzeitende T = 0 einen Kurs von St = 120, also größer gleich dem Basispreis, wird dem Halter der Option der Payoff Q = 10 ausgezahlt.
- Hat die Aktie A aber zum Laufzeitende T = 0 einen unter dem Basispreis X = 100 liegenden Kurs von St = 90 verfällt die Option.
Eine Bewertung einer Kaufoption vor dem Verfallszeitpunkt ist durch die gängige Black-Scholes-Formel möglich (Verkaufsoption durch Vorzeichenwechsel von d2):
Asset-or-Nothing-Option
Die Asset-or-Nothing-Kaufoption hat einen Payoff gleich dem zugrundeliegenden Basiskurs, wenn der Basiskurs im Verfallszeitpunkt über oder gleich dem vereinbarten Basispreis ist. Die Option verfällt, wenn der Basiskurs im Verfallszeitpunkt darunter liegt. Auch hier verhält sich die Verkaufsoption umgekehrt.
Eine reguläre europäische Kaufoption (Call) kann mit dem Kauf (Long-Position) einer Asset-or-Nothing-Kaufoption und dem Verkauf (Short-Position) einer Cash-or-Nothing-Kaufoption mit einem Payoff gleich dem Basispreis der Asset-or-Nothing-Option realisiert werden.
Beispiel: Eine Asset-or-Nothing-Kaufoption auf den Basispreis X = 100 einer Aktie A mit einer Laufzeit von T = 1 Jahr ist folgendes Wert:
- Hat die Aktie A zum Laufzeitende T = 0 einen Kurs von St = 120, also größer gleich dem Basispreis, wird dem Halter der Option der Payoff Q = ST = 120 ausgezahlt.
- Hat die Aktie A aber zum Laufzeitende T = 0 einen unter dem Basispreis X = 100 liegenden Kurs von St = 90 verfällt die Option.
Der Wert der Kaufoption vor dem Verfallszeitpunkt ist wiederum auch hier durch die Black-Scholes-Formel möglich, wobei der Payoff Q hier durch den Basiskurs S ersetzt wird (Verkaufsoption durch Vorzeichenwechsel von d1):
Wikimedia Foundation.