- Glucose-6-Phosphatase
-
Glucose-6-Phosphatase —
Masse/Länge Primärstruktur 357 Aminosäuren Isoformen G6Pase, G6Pase-2, G6Pase-3 Bezeichner Gen-Name(n) G6PC, G6PC2, G6PC3 Externe IDs OMIM: 232200 UniProt: P35575 Enzymklassifikation EC, Kategorie 3.1.3.9 Phosphatase Reaktionsart Hydrolyse einer Phosphorsäureester-Bindung Substrat D-Glucose-6-phosphat + H2O Produkte D-Glucose + Phosphat Vorkommen Homologie-Familie G6Pase Übergeordnetes Taxon Euteleostomi Glucose-6-Phosphatase (Abk.: G6Pase, Gen: G6PC) ist der Name des Enzyms, das die Abspaltung von Phosphat von Glucose-6-phosphat (G6P) katalysiert. Diese Reaktion ist ein unentbehrlicher Teilschritt mehrerer Energiestoffwechselwege in Wirbeltieren. Im Menschen werden drei Isoformen des Enzyms produziert, die von den Genen G6PC, G6PC2 und G6PC3 codiert werden; die entsprechenden Enzyme heißen G6Pase, G6Pase-2 und G6Pase-3. G6Pase ist beim Menschen in der Leber, den Nieren und in geringen Mengen im Darm anzutreffen, G6Pase-2 ist spezifisch in Inselzellen lokalisiert, die Enzymaktivität der G6Pase-3 ist zweifelhaft. Mutationen in G6PC sind verantwortlich für von-Gierke-Krankheit Typ Ia, und Variationen in G6PC2 sind assoziiert mit hohem Glucoselevel während des Fastens (FGQTL1, >5,55 mmol/l Glucose), einem Risikofaktor für Diabetes mellitus; Mangel an G6PC-3 schließlich kann zu schwerer familiärer Neutropenie Typ 4 (SCN4) führen.[1]
Die G6Pasen sind Membranproteine im endoplasmatischen Reticulum (ER), die zusammen mit Glucose-6-phosphat-Translokase einen Proteinkomplex bilden. Dieser Komplex sorgt gleichzeitig für das Einfließen von G6P ins Innere (Lumen) des ER, und für die Hydrolyse von G6P zu Glucose und Phosphat. Schlussendlich wird die Glucose aus dem ER transportiert, der genaue Mechanismus ist aber noch unbekannt (2008).[1][2]
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Katalysierte Reaktion
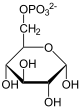
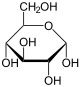
G6P wird zu Glucose hydrolysiert. Die Reaktion ist praktisch irreversibel.[3]
Die Reaktion ist Teilschritt der Gluconeogenese.
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ a b UniProt P35575, UniProt Q9NQR9, UniProt Q9BUM1
- ↑ D'Eustachio/Harris/reactome.org: Efflux of glucose from the endoplasmic reticulum
- ↑ Harris/reactome.org: alpha-D-Glucose 6-phosphate + H2O ⇒ alpha-D-Glucose + Orthophosphate
Literatur
- Cohn RM, Herman RH, Zakim D: Glucose 6-phosphatase: a multifunctional enzyme. In: Am. J. Clin. Nutr.. 22, Nr. 9, September 1969, S. 1204–10. PMID 4309941.
Weblinks
 Wikibooks: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie: Glucose-6-Phosphatase – Lern- und LehrmaterialienKategorien:
Wikibooks: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie: Glucose-6-Phosphatase – Lern- und LehrmaterialienKategorien:- Phosphatase
- Krankheitsassoziiertes Protein
Wikimedia Foundation.