- 2-Methylpropan-1-ol
-
Strukturformel 
Allgemeines Name 2-Methyl-1-propanol Andere Namen - i-Butanol
- iso-Butanol
- Isobutanol
- Isobutylalkohol
- 2-Methylpropan-1-ol
Summenformel C4H10O CAS-Nummer 78-83-1 Kurzbeschreibung farblose Flüssigkeit mit fuselölartigem Geruch [1] Eigenschaften Molare Masse 74,12 g·mol−1 Aggregatzustand flüssig
Dichte 0,80 g·cm−3 [1]
Schmelzpunkt −107,8 °C [1]
Siedepunkt 108 °C [1]
Dampfdruck 12 hPa (20 °C) [1]
Löslichkeit löslich in Wasser: 95 g·l−1 (20 °C) [1]
Sicherheitshinweise Gefahrstoffkennzeichnung aus RL 67/548/EWG, Anh. I [2] 
Reizend (Xi) R- und S-Sätze R: 10-37/38-41-67 S: (2)-7/9-13-26-37/39-46 MAK 310 mg·m-3 bzw. 100 ml·m−3 [1]
WGK 1 – schwach wassergefährdend Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. 2-Methyl-1-propanol (auch i-Butanol oder Isobutanol) ist ein aliphatischer Kohlenwasserstoff und gehört zur Gruppe der Alkanole, die wiederum zu den Alkoholen gehören.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Gewinnung und Darstellung
Isobutanol kann mit Hilfe von Mikroorganismen biotechnologisch hergestellt werden. Dann dient es ähnlich wie 1-Butanol als regenerativer Biokraftstoff mit hervorragenden Eigenschaften[3]
Chemisch gewinnt man Isobutanol wie auch 1-Butanol durch Hydroformylierung von Propen. Im Gegensatz zur Gewinnung von 1-Butanol arbeitet man hier mit dem anderen Reaktionsprodukt weiter und hydriert es:
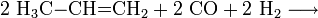
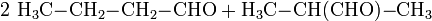
- Propen reagiert mit Kohlenstoffmonoxid und Wasserstoff zu Butanal und 2-Methylpropanal.
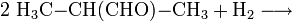
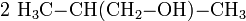
- Das entstandene 2-Methylpropanal reagiert mit Wasserstoff zu 2-Methyl-1-propanol weiter.
Eigenschaften
Physikalische Eigenschaften
2-Methyl-1-propanol ist eine farblose Flüssigkeit, die süßlich riecht. Wie alle Butanole ist auch 2-Methyl-1-propanol brennbar. Man kann 2-Methyl-1-propanol mit allen gängigen organischen Lösungsmitteln wie Ether, Glykol, Alkoholen, Ketonen und Aldehyden beliebig mischen, in Wasser ist es jedoch nur begrenzt löslich.
Chemische Eigenschaften
- Reaktionen
Mögliche Reaktionen des 2-Methyl-1-propanol sind die Veresterung zu einem Ester oder die Dehydrierung zu einem Aldehyd.
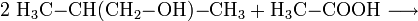
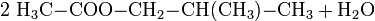
- 2-Methyl-1-propanol reagiert mit Ethansäure zu Ethansäure 2-methyl-propylester und Wasser.
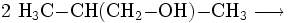
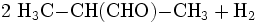
- 2-Methyl-1-propanol reagiert zu 2-Methylpropanal und Wasserstoff.
Verwendung
Verwendung findet 2-Methyl-1-propanol in Derivaten als Lösungsmittel, vorwiegend in der Lackindustrie. Es verbessert die Eigenschaften der Lacke.
Quellen
- ↑ a b c d e f g Eintrag zu 2-Methyl-1-propanol in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des BGIA, abgerufen am 10. Sep. 2007 (JavaScript erforderlich)
- ↑ Eintrag zu CAS-Nr. 78-83-1 im European chemical Substances Information System ESIS
- ↑ http://www.spiegel.de/wissenschaft/natur/0,1518,572186,00.html
Weblinks
Wikimedia Foundation.
