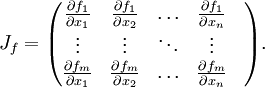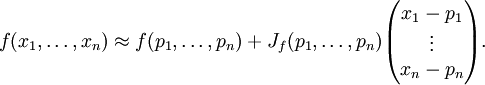- Jacobian
-
Die Jacobi-Matrix (benannt nach Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi; auch Funktionalmatrix oder Ableitungsmatrix genannt) einer differenzierbaren Funktion
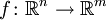 ist die
ist die 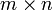 -Matrix sämtlicher erster partieller Ableitungen. Sie ist eine Darstellungsmatrix, also die Darstellung einer linearen Abbildung mittels einer Matrix, der Ableitung der Funktion f, wenn man als Basis die Standardbasis verwendet. Genutzt wird sie z. B. zur annähernden Berechnung (Approximation) oder Minimierung mehrdimensionaler Funktionen in der Mathematik. Sie wird mit Jf , Df oder
-Matrix sämtlicher erster partieller Ableitungen. Sie ist eine Darstellungsmatrix, also die Darstellung einer linearen Abbildung mittels einer Matrix, der Ableitung der Funktion f, wenn man als Basis die Standardbasis verwendet. Genutzt wird sie z. B. zur annähernden Berechnung (Approximation) oder Minimierung mehrdimensionaler Funktionen in der Mathematik. Sie wird mit Jf , Df oder 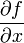 bezeichnet.
bezeichnet.Inhaltsverzeichnis
Bildung
Bezeichnet man die Koordinaten im Urbildraum
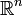 mit
mit 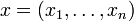 und die Komponentenfunktionen von f mit
und die Komponentenfunktionen von f mit 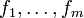 , so lautet die Jacobi-Matrix
, so lautet die Jacobi-Matrix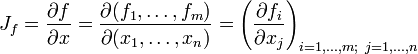 ,
,
beziehungsweise ausführlich
Um sich leichter merken zu können, in welche Richtung der Index der Koordinaten anwächst und in welche Richtung der Index der Komponentenfunktionen anwächst, kann man die nachfolgende Schreibweise verwenden. Schreibt man
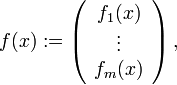 dann ist die Jacobimatrix in Spaltenschreibweise gegeben durch
dann ist die Jacobimatrix in Spaltenschreibweise gegeben durch 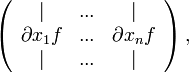 wobei natürlich
wobei natürlich 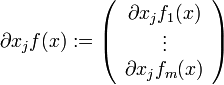 die partiellen Ableitungen der vektorwertigen Funktion f nach der jeweiligen Koordinate darstellt.
die partiellen Ableitungen der vektorwertigen Funktion f nach der jeweiligen Koordinate darstellt.Man beachte weiterhin, dass die j-te Zeile der Jacobimatrix den transponierten Gradienten der Komponentenfunktion fj enthält.
Beispiel
Wir betrachten die Funktion
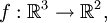 die gegeben ist durch
die gegeben ist durch 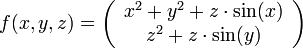
Dann ist
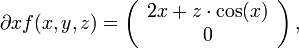
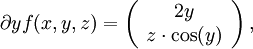
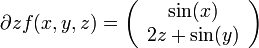
und damit die Jacobi-Matrix
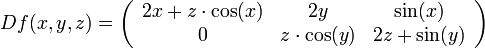
Anwendungen
Sie kann, wenn man sie für einen Punkt
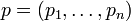 ausrechnet, zur Näherung der Funktionswerte von f in der Nähe von p verwendet werden:
ausrechnet, zur Näherung der Funktionswerte von f in der Nähe von p verwendet werden:Diese affine Abbildung entspricht der Taylor-Approximation erster Ordnung (Linearisierung).
Für m = 1 entspricht die Jacobi-Matrix dem Gradienten von f. Je nach Definition des Gradienten, der manchmal als Zeilenvektor und manchmal als Spaltenvektor definiert wird, unterscheidet sich jedoch in diesem Fall die Jacobi-Matrix als Zeilenvektor vom Gradienten.
Ein Beispiel für eine Rechnung mit der Jacobi-Matrix ist die Transformation in Polarkoordinaten.
Weiterhin lässt sich die Jacobimatrix zu Berechnung von Extremstellen in der mehrdimensionalen Analysis benutzen. Eine notwendige Bedingung für das Vorhandensein lokaler Extremstellen einer differenzierbaren Funktion auf einer offenen Definitionsmenge D,
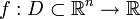 , ist durch Df(x) = (gradf)T(x) = 0 gegeben.
, ist durch Df(x) = (gradf)T(x) = 0 gegeben.Determinante der Jacobi-Matrix
Für den Fall m = n ist f eine
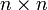 -Abbildung, und die Jacobi-Matrix ist quadratisch. In diesem Fall kann man die Determinante der Jacobi-Matrix berechnen. Die Determinante der Jacobi-Matrix wird Jacobi-Determinante oder Funktionaldeterminante genannt und spielt z. B. bei Transformationen von Integralen eine wichtige Rolle.
-Abbildung, und die Jacobi-Matrix ist quadratisch. In diesem Fall kann man die Determinante der Jacobi-Matrix berechnen. Die Determinante der Jacobi-Matrix wird Jacobi-Determinante oder Funktionaldeterminante genannt und spielt z. B. bei Transformationen von Integralen eine wichtige Rolle.Siehe auch
Wikimedia Foundation.