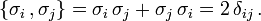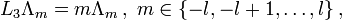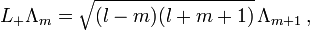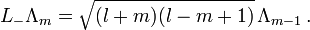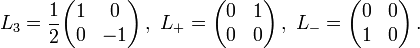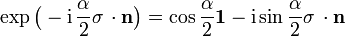- Pauli-Matrix
-
Die Pauli-Matrizen σ1,σ2,σ3 (nach Wolfgang Pauli) bilden eine Basis der hermiteschen, spurfreien 2×2–Matrizen und stellen die Wirkung der Drehimpulsoperatoren,
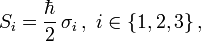 auf Spin-1/2-Zuständen, beispielsweise auf Elektronen, dar.
auf Spin-1/2-Zuständen, beispielsweise auf Elektronen, dar.Die Pauli-Matrizen lauten
Sie erfüllen die Algebra
(Schreibweise in einsteinscher Summenkonvention),
also insbesondere bis auf einen Faktor 2 die Drehimpulsalgebraund die Clifford- oder Dirac-Algebra
Die Pauli-Matrizen gehören zum Spezialfall l = 1 / 2 von Drehimpulsoperatoren, die auf Basisvektoren Λm eines Drehimpuls-l-Multipletts mit Quantenzahlen m in Maßsystemen mit
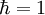 folgendermaßen wirken
folgendermaßen wirkenDabei ist 2l + 1 eine natürliche Zahl und für m treten die 2l + 1 verschiedenen Quantenzahlen
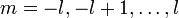 auf. Für l = 1 / 2 wirken die Drehimpulsoperatoren auf die Komponenten von Linearkombinationen der beiden Basisvektoren Λ1 / 2 und Λ − 1 / 2 demnach durch Multiplikation mit den folgenden Matrizen
auf. Für l = 1 / 2 wirken die Drehimpulsoperatoren auf die Komponenten von Linearkombinationen der beiden Basisvektoren Λ1 / 2 und Λ − 1 / 2 demnach durch Multiplikation mit den folgenden MatrizenMit
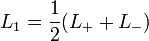 und
und 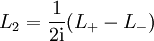 ergibt sich dann, dass die Drehimpulsoperatoren auf die Komponenten von Spin-1/2-Zuständen durch Multiplikation mit den halben Pauli-Matrizen wirken.
ergibt sich dann, dass die Drehimpulsoperatoren auf die Komponenten von Spin-1/2-Zuständen durch Multiplikation mit den halben Pauli-Matrizen wirken.Zugeordnete Drehgruppe
Die drei Pauli-Matrizen σi, mit der zugehörigen Lie-Algebra, erzeugen die komplexe Drehgruppe SU(2) mit Elementen
wobei die Drehachse
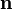 ein Einheitsvektor im
ein Einheitsvektor im 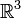 ist und α der Drehwinkel, der von 0 bis
ist und α der Drehwinkel, der von 0 bis 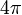 läuft. In der Tat ergibt sich
läuft. In der Tat ergibt sich 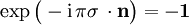 . Erst die Drehung um 4π reproduziert jeden Spin-1/2-Zustand.
. Erst die Drehung um 4π reproduziert jeden Spin-1/2-Zustand.Siehe auch
Weblinks
- Eric W. Weisstein: Pauli Matrices auf MathWorld (englisch)
Wikimedia Foundation.

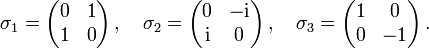
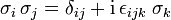
![[\sigma_i\, ,\sigma_j] = \sigma_i \, \sigma_j - \sigma_j \, \sigma_i = 2\, \mathrm i\, \epsilon_{ijk}\; \sigma_k\,](/pictures/dewiki/57/97b5542b942e7325822ac313040776dd.png)