- Delay-Code
-
Die digitale Frequenzmodulation, abgekürtzt FM und auch als Miller-Code oder Delay-Code bezeichnet, ist eine digitale Modulation bzw. Leitungscodierung und liefert im Gegensatz zur Frequenzmodulation kein analoges und kontinuierliches moduliertes Signal, sondern eine zeitdiskrete digitale Bitfolge. Sie wird unter anderem bei magnetischen Datenträgern wie Disketten als Kanalcode für die Datenaufzeichnung verwendet.
In der Fachliteratur ist die Trennung zwischen der Modulation und der Leitungscodierung in diesem Grenzbereich nicht eindeutig und so wird dieses Verfahren sowohl als eine Form der Modulation als auch als eine Art der Kanalcodierung bezeichnet.
Die digitale Frequenzmodulation (FM) ist mit der Modified Frequency Modulation (MFM) verwandt und stellt deren Vorläufer dar. Im Gegensatz zur MFM weist die FM allerdings im Spektrum höhere Frequenzanteile auf und erfordert damit größere Bandbreiten bei der magnetischen Speichermedien. Im Gegensatz zu der ebenfalls verwandten Manchester-Codierung ist das Frequenzspektrum der FM reduziert, es ist aber nicht gleichanteilsfrei. Die für magnetische Aufzeichnung notwendige Gleichanteilsfreiheit des Signals muss daher durch eine zusätzliche Kanalcodierung gewährleistet werden.
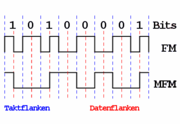
Bei der FM erfolgt nach jedem Nutzdatenbit, egal ob logisch-1 oder logisch-0, ein Signalwechsel. Bei einem logisch-1 Bit erfolgt zusätzlich noch ein Signalwechsel in der Bitmitte, wie in nebenstehender Abbildung oben dargestellt. Daher kann diese Codierung auch als eine Frequenzmodulation aufgefasst werden: Den logisch-0 Bits wird eine niedrige Frequenz f0=1/2T zugewiesen und den logisch-1 Bits wird eine hohe Frequenz f1=1/T zugewiesen. T stellt die Periodendauer eines Bits dar. Andere Frequenzzuweisungen sind nicht vorgesehen.
Schreibverfahren für magnetische und optische DatenträgerPhysisch: Magnetisierung | Longitudinal Recording | Perpendicular Recording | GMR-Effekt | TMR-Effekt
Logisch: Frequency Modulation (FM) | Modified Frequency Modulation (MFM) | Non Return to Zero (NRZ) | Group Coded Recording (GCR) | Run Length Limited (RLL) | Partial Response/Maximum Likelihood (PRML) | Extended Partial Response/Maximum Likelihood (EPRML) | Eight-to-Fourteen-Modulation (EFM)
Wikimedia Foundation.