- Ganglioside
-
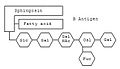
Ganglioside [1][2][3][4][5][6]sind Sphingolipide, die über ihren Lipidanteil in der äußeren Zellmembran verankert sind. Ihr strukturelles Grundgerüst wird vom Aminodialkohol Sphingosin gebildet. Grob dargestellt enthalten Ganglioside ein komplexes Oligosaccharid, eine langkettige Fettsäure und das Sphingosin Grundgerüst.
Im Gegensatz zu den Cerebrosiden handelt es sich um komplexere Sphingolipide, die verzweigte Zuckerketten mit bis zu sieben Zuckerresten aufweisen. Durch diese nach außen ragenden Zuckerreste, insbesondere durch negativ geladene Sialinsäuren, bestimmen sie die Eigenschaften der Zelloberfläche mit.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Vorkommen
Die höchste Konzentrationen an Gangliosiden findet man im Nervensystem, speziell in der grauen Substanz des Gehirns, wo sie 6% aller Lipide ausmachen. Im Nervensystem ist eine Vielzahl verschiedener Ganglioside angereichert, deren Zusammensetzung sich im Laufe der Entwicklung und bei Anpassung an sich ändernde Umweltbedingungen wie z.B. schwankende Temperaturen verändert.[7]
Medizinischer Nutzen
Neben der postulierten Bedeutung bei der neuronalen Informationsübertragung und -speicherung stellen Ganglioside auch wichtige Tumormarker dar. Das Auftreten von Gangliosiden bei vielen Krebserkrankungen deutet auch auf eine Rolle dieser Glykolipide bei der Progression von Tumorerkrankungen hin. Über welche molekularen Mechanismen Ganglioside wirken, ist jedoch nach wie vor unklar.
Blutgruppe
Anhand bestimmter Ganglioside kann man die Blutgruppe bestimmen. Am Sphingosin-Grundgerüst hängt wie bei jedem Sphingolipid eine Fettsäure. Die Besonderheit der Ganglioside sind die komplexen Oligosaccharide die an das Sauerstoffatom geknüpft sind. Je nachdem welche Kombination aus Monosacchariden verknüpft ist bestimmt die Blutgruppe. Die Kombination Glucose (Glc) – Galactose (Gal) – N-Acetylgalactosamin (GalNAc) – Galactose – Fucose (Fuc) kodiert beispielsweise für die Blutgruppe 0. Ist an die Kette noch ein weiteres N-Acetylgalactosamin angehängt kodiert es für die Blutgruppe A. Ist stattdessen eine weitere Galactose angehängt für die Blutgruppe B.
Abbau und Pathologie
Der Gangliosidabbau findet in den Lysosomen statt. Er erfolgt durch hochspezifische Glykosylhydrolasen, die sequenziell die endständigen Zuckerreste abspalten. Das GM1-Gangliosid ist das Stammgangliosid, als Intermediärprodukte entstehen beim Abbau GM2- und GM3-Gangliosid. Störungen des Gangliosidabbaus können zu schwerwiegenden Erkrankungen (lysosomale Speicherkrankheiten), den Sphingolipidosen, führen. Die durch die β-Galactosidase-Defizienz bedingte Anhäufung von GM1-Gangliosid im Zentralnervensystem erklärt die progressive zerebrale Symptomatik bei Patienten mit GM1-Gangliosidose. Für den Abbau des GM2-Gangliosids sind Hexosaminidasen A und B zuständig. So endet der Defekt der Hexosaminidase A bei der autosomal-rezessiv vererbten Tay-Sachs-Krankheit, die mit einer Erhöhung der Konzentration des Gangliosids GM2 einhergeht, unbehandelt vor Erreichen des dritten Lebensjahres tödlich. Durch Amniozentese und Untersuchung der Amnionflüssigkeit auf Beta-N-Acetylhexosaminidaseaktivität kann die Tay-Sachs-Krankheit jedoch schon während der fetalen Entwicklungsphase diagnostiziert werden. Ein Mangel an α-Galactosidase A bewirkt eine Ansammlung von Globotriaosylceramid, wodurch der Morbus Fabry verursacht wird.
Bibliographie
- ↑ Gangliosides as components of lipid membrane domains. Glycobiology 17(1):1R-13R (2007), PMID 16982663.
- ↑ Combinatorial ganglioside biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 277(29):25859-62 (2002), PMID 12011101.
- ↑ Ganglioside metabolism. Enzymology, Topology, and regulation. J Biol Chem 268(8):5341-4 (1993), PMID 8449895.
- ↑ Role of ganglioside metabolism in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease--a review. J Lipid Res 49(6):1157-75 (2008), PMID 18334715.
- ↑ Thematic review series: sphingolipids. Ganglioside GM3 suppresses the proangiogenic effects of vascular endothelial growth factor and ganglioside GD1a. J Lipid Res 49(5):929-38 (2008), PMID 18287616.
- ↑ Regulation of ganglioside biosynthesis in the nervous system. J Lipid Res 45(5):783-93 (2004), PMID 15087476.
- ↑ Peter Nuhn: Naturstoffchemie, 2. Auflage, S. Hirzel Wissenschaftliche Verlagsgesellschaft Stuttgart, 1990, S. 324−326, ISBN 3-7776-0473-9.
Wikimedia Foundation.