- Glycogenin
-
Glycogenin —
Masse/Länge Primärstruktur 349 Aminosäuren Sekundär- bis Quartärstruktur Homodimer Kofaktor Mangan Isoformen GN-1L, GN-1, GN-1S, GN-2α, GN-2β, GN-2γ, GN-2δ, GN-2ε, GN-2ζ Bezeichner Gen-Name(n) GYG1, GYG2 Externe IDs OMIM: 603942 UniProt: P46976 Enzymklassifikation EC, Kategorie 2.4.1.186 Glycosyltransferase Reaktionsart Übertragung eines Glucose-Rests Substrat Glucosyln-Glycogenin + UDP-Glucose (n=0-12) Produkte Glucosyln+1-Glycogenin + UDP Vorkommen Homologie-Familie Glycogenin Übergeordnetes Taxon Pilze/Vielzeller Glycogenin heißen Enzyme, die sich selbst Glucose-Reste anhängen - die Polysaccharidkette kann bis zu 13 Glucoseeinheiten lang werden. Diese Reaktion ist notwendig, um die Erzeugung langkettiger Polysaccharide, insbesondere Glycogen, in Gang zu bringen, denn das Enzym Glykogen-Synthase kann nur arbeiten, wenn bereits kurze Ketten vorhanden sind. Glycogenine gibt es in Pilzen und Vielzellern. Menschen haben zwei homologe Gene, die jeweils mehrere Isoformen des Enzyms ermöglichen, die in verschiedenen Gewebetypen lokalisiert sind. Glycogenin ist fest an Glycogensynthase gebunden, kann also als ihr Kofaktor bezeichnet werden. Mutationen im GYG1-Gen sind für eine erbliche Glykogenspeicherkrankheit verantwortlich.[1][2]
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Katalysierte Reaktionen
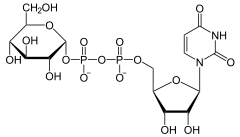
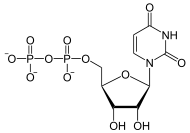
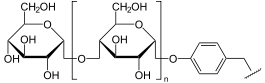
Glycogenin katalysiert die Addition von Glucose an sich selbst, indem es die erste UDP-Glucose, gebildet aus UTP und Glucose, an den Tyr-194-Rest seines aktiven Zentrums bindet. Dabei entsteht UDP.
Danach reiht das Enzym weitere Glucosereste bis zu einem gewissen Limit (ca. 5-13) an, ab dessen Erreichen die Glycogensynthase die weitere Polymerisation übernimmt. Das Glycogenin bleibt an der Glycogenkette gebunden. Nach eventuellem Abbau der Kette steht das Enzym als Keimzelle für erneute Glycogensynthese zur Verfügung, d. h. es wird nicht mit abgebaut.[3][4]
Siehe auch
Insulin -- Blutzucker -- Glykogenspeicherkrankheit
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ UniProt P46976, UniProt O15488
- ↑ Skurat AV, Dietrich AD, Roach PJ: Interaction between glycogenin and glycogen synthase. In: Arch. Biochem. Biophys.. 456, Nr. 1, Dezember 2006, S. 93–7. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2006.09.024. PMID 17055998. Volltext bei PMC: 1769445.
- ↑ Hurley TD, Walls C, Bennett JR, Roach PJ, Wang M: Direct detection of glycogenin reaction products during glycogen initiation. In: Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.. 348, Nr. 2, September 2006, S. 374–8. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.106. PMID 16889748. Volltext bei PMC: 1635985.
- ↑ Wilson RJ, Gusba JE, Robinson DL, Graham TE: Glycogenin protein and mRNA expression in response to changing glycogen concentration in exercise and recovery. In: Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.. 292, Nr. 6, Juni 2007, S. E1815–22. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00598.2006. PMID 17311895.
Weblinks
 Wikibooks: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie: Glycogensynthese – Lern- und LehrmaterialienKategorien:
Wikibooks: Biochemie und Pathobiochemie: Glycogensynthese – Lern- und LehrmaterialienKategorien:- Glycosyltransferase
- Krankheitsassoziiertes Protein
Wikimedia Foundation.