- Vinylamin
-
Strukturformel 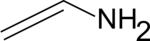
Allgemeines Name Vinylamin Andere Namen - Aminoethen
- Aminoethylen
- Ethenamin (IUPAC)
Summenformel C2H5N CAS-Nummer 593-67-9 PubChem 11642 Eigenschaften Molare Masse 43,07 g·mol−1 Sicherheitshinweise EU-Gefahrstoffkennzeichnung [1] keine Einstufung verfügbar R- und S-Sätze R: siehe oben S: siehe oben Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen. Vinylamin, auch als Aminoethen, Aminoethylen oder Ethenamin bezeichnet, ist ein Amin mit der chemischen Formel C2H5N beziehungsweise H2C=CH-NH2.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
Herstellung und Eigenschaften
Vinylamin existiert als Tautomer von Ethylidenimin. Beide Tautomere, das Enamin Vinylamin sowie das entsprechende Imin Ethylidenimin, sind instabil. Ethylidenimin lässt sich beispielsweise als Umlagerungs- beziehungsweise Zersetzungsprodukt von Ethylenimin oder 2,4,6-Trimethyl-[1,3,5]triazin, kurzzeitig in der Gasphase synthetisieren.[2]
Vinylamin ist das Basismonomer von Polyvinylamin (PVAm). Die Synthese von PVAm erfolgt jedoch über die Polymerisation von N-Vinylformamid mit anschließender Hydrolyse, da Vinylamin selbst nicht zugänglich ist.
Einzelnachweise
- ↑ In Bezug auf ihre Gefährlichkeit wurde die Substanz von der EU noch nicht eingestuft, eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- ↑ I. Stolkin u. a.: N-methylmethyleneimine and ethylideneimine: Gas- and matrix-infrared spectra, AB initio calculations and thermodynamic properties. In: Chemical Physics 21/1977, S. 327–347.
Literatur
- D. Mcnaughton, E. G. Robertson: The Far-Infrared Inversion Transition of Vinylamine. In: Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy 163/1994, S. 80–85.
- S. Saebo¸, L. Radom: The structure of vinylamine. In: Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM 89/1982, S. 227–233.
- S.F. Dyke The Chemistry of Enamines, Cambridge University Press, London, 1973.
- F. J. Lovas u. a.: Pyrolysis of ethylamine. I. Microwave spectrum and molecular constants of vinylamine. In: J. Chem. Phys. 62/1975, S. 1925.
- R. Meyer: The Inversion of the Amino Group in Vinylamine, a Flexible Model Treatment. In: Helvetica Chimica Acta 61/1978, S. 1418–1426.
- M. R. Ellenberger u. a.: Proton affinities of ethylidenimine and vinylamine. In: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 101/1979, S. 7151–7154.
- C. N. Sanrama u. a.: Evaluation of reactive and nonreactive paths for the interaction between 1O2(1Δg) and vinylamine using semiempirical methods. In: Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM 367/1996, S. 119–126.
Weblinks
- Ethenylamine Landolt-Börnstein, Universität Hamburg
Wikimedia Foundation.

